Current Classroom Assessment Challenges
Classroom assessment is one of the cornerstones of effective teaching and learning, serving as a rich source of information regarding student growth and a guide for instructional decisions. Traditional exit tickets or homework have long faced challenges with inconsistency, subjectivity, or misalignment with learning objectives.
Rubric-based grading (RBG) offers promising solutions by focusing on assessing students’ proficiency on a set of learning standards (standards-based grading) or mastery of concepts and skills (mastery-based grading). Rubric-based grading also provides opportunities for educators to diagnose challenges students face in their learning journey and offer detailed feedback (Beachboard & Kersey, 2022; Muñoz, & Guskey, 2015).
RBG presents implementation challenges for many teachers, including cognitive difficulties in differentiating academic performance levels, time-consuming grading and reporting processes, and challenges in communicating the results with students and parents. Creating high-quality rubrics, while essential for fair and informative assessment, remains a complex and time-consuming process for educators.
Colleague AI Scaffolds Teachers into Future Classroom Assessment
Colleague AI introduces its innovative, unique solution through its Rubric Generation function and AI-assisted grading. This AI-assisted assessment procedure transforms the types of assessment educators offer to students, and emphasizes students’ learning progression, higher-order cognitive skills (such as strategic and extended thinking). The platform utilizes technological innovations that embed contextual knowledge from educational standards and theoretical frameworks to ensure consistent alignment with learning objectives.
Colleague AI supports rubric-based grading practice:
- Aligning with learning objective or standards. The assessment procedure generates rubrics aligning with Common Core State Standards (CCSS), Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS), and state-specific learning standards to ensure measurable student outcomes. We allow teachers to choose various instructional frameworks, including Bloom’s Taxonomy, Depth of Knowledge, or other teacher-defined framework.
- Scale levels. Colleague AI offers multiple instructional and rubrics framework for teachers to choose or define their own.
- The scoring report typically uses a 1-4 or 1-5 scale to measure a student’s level of learning progression.
- With clear definitions for each level, students themselves can use them to assess their own work.
- Responsive learning. Colleague AI, in collaboration with teachers, ensures all students receive prompt, tailored feedback, supporting their learning progress, which is particularly important for at-risk students (Fredricks, Blumenfeld, & Paris, 2004)
- The reporting focuses on the strengths the student demonstrated and areas for improvement.
- Redo and Reassessment. It also emphasizes the importance of providing students with time and opportunities to redo assignments and reassess their understanding of concepts. Track learning progression towards mastery on specific standards.
- Tracking student performance on formative assessments allows for data-driven instruction (Mandinach & Gummer, 2013).
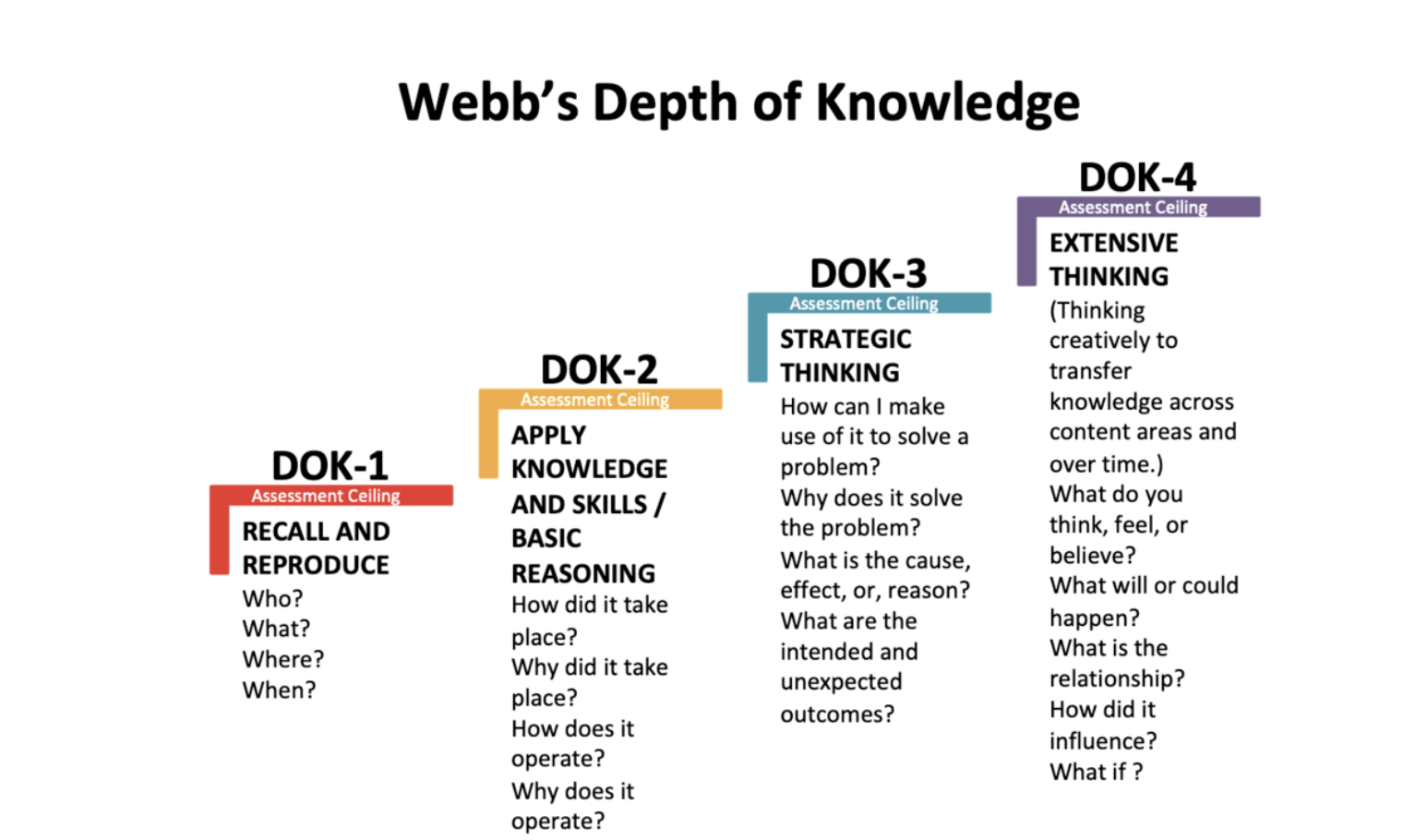
Caption: Webb’s Depth of Knowledge as One Framework to Guide Rubric Generation and Grading
How It Works in Ms. Johnson’s Middle School Science Class
Meet Ms. Johnson, a dedicated middle school science teacher preparing for her unit on photosynthesis. Like many educators, she previously invested significant time creating rubrics to ensure fair and thorough assessment of her students’ understanding of this crucial biological process. This year, she’s leveraging Colleague AI’s Rubric Generation function to enhance her assessment planning.
As she begins her preparation, Ms. Johnson follows her structured workflow:
Step 1: Building the Standards-Based Rubric
- She inputs the relevant NGSS standards for photosynthesis into Colleague AI’s Rubric Generation, focusing on MS-LS1-6 (constructing scientific explanations about the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of matter and energy flow).
- If she already has an assessment, she can select the option to generate specific rubrics for the assessment.
Step 2. Implementing an Instructional Framework
- Ms. Johnson selects the Depth of Framework that emphasizes on advanced cognitive thinking (e.g., strategic and extended thinking) and scientific inquiry skills.
- She includes specific criteria for lab work, scientific diagrams, and written explanations about the photosynthesis process.
Step 3. Incorporating Accessibility Requirements. For her students with visual disabilities, she specifies the need for:
- Alternative assessment methods for diagram-based questions.
- Audio descriptions of visual concepts.
Step 4. Teachers’ Refinement to Ensure Accuracy, Relevance, and Usefulness. Once Colleague.ai generates the draft rubrics, Ms. Johnson uses the full editing function and her professional knowledge to validate the rubrics, ensuring accuracy of scientific knowledge and relevance to her classroom context, learning standards, and learning objectives of this unit.
Step 5. AI-Assisted Grading. Once the rubrics are finalized, Ms. Johnson can utilize a specialized AI tool to grade students’ responses, both handwritten and digital, within seconds. The assessment report includes not only scores based on the rubrics but also detailed justifications for each evaluation, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. This detailed report is written in clear, actionable language. Teachers can then modify, finalize, and return to students.
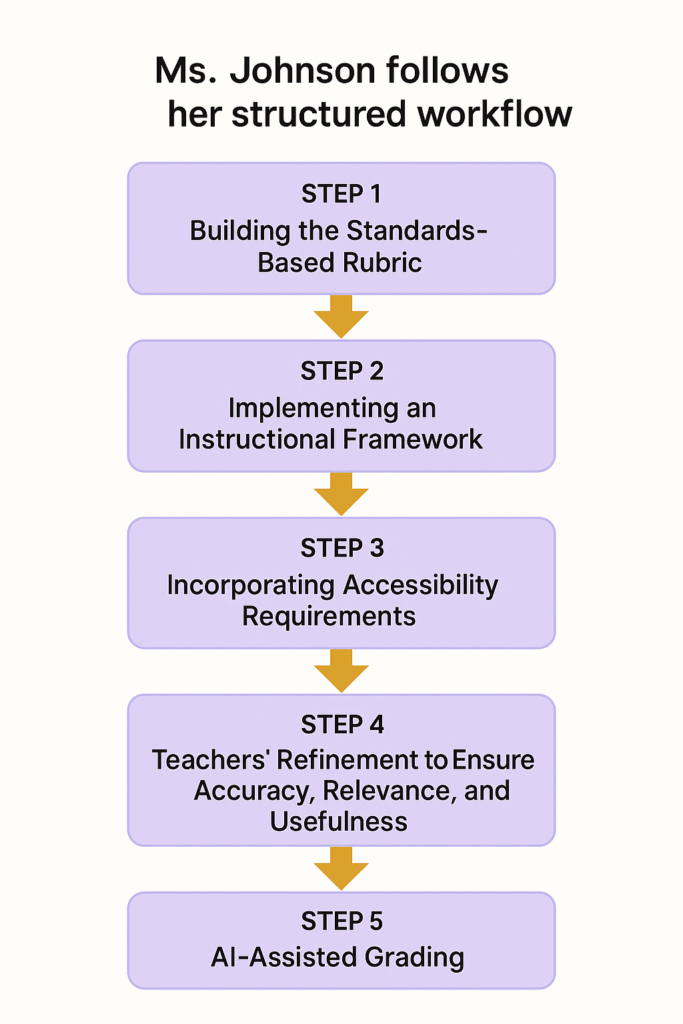
Caption: Ms. Johnson’s Workflow of AI-Assisted Rubric Generation and Grading
Preserving Educator Autonomy While Enhancing Efficiency
The beauty of Colleague AI’s approach lies in its balance between automation and teacher control. Here’s how Ms. Johnson maintains her autonomy:
- Customization Control: While the system generates initial rubrics, Ms. Johnson can modify every aspect to match her teaching style and student needs.
- Assessment Flexibility: She decides whether to allow students to get AI feedback first, then modify and resubmit their work for formative assessments, or to reserve the AI grading function solely for herself during summative assessments.
- Final Decision-Making: No grades are released to students without her review and approval.
- High-Yielding Tasks Optimization: She can use her saved time from grading to have a meaningful discourse with each student.
A New Chapter in Assessment
The integration of Colleague AI’s rubric generation function represents more than just technological advancement. It is a transformation in how we approach assessment while maintaining the crucial role of teacher expertise. As Ms. Johnson’s experience shows, when technology supports rather than supplants teacher judgment, the result is more effective, personalized, and growth-oriented education.
Try Colleague AI For Free
Ready to revolutionize your assessment practice? Try Colleague AI for free today and experience how it simplifies the grading process while delivering personalized, growth-oriented feedback.
Or, watch this tutorial video to see it in action and discover why it’s the best AI tool for teachers.
Citations and Resources
Beachboard & Kersey (2022). Getting Started With Standards-Based Grading. https://www.edutopia.org/article/getting-started-standards-based-grading/
Muñoz, M. A., & Guskey, T. R. (2015). Standards-based grading and reporting will improve education. Phi Delta Kappan, 96(7), 64-68.
Webb’s depth of knowledge. (n.d.). Structural Learning. Retrieved January 24, 2024, from https://www.structural-learning.com/post/webbs-depth-of-knowledge
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 59-109.





